Documentation is currently for moon v2 and latest proto. Documentation for moon v1 has been frozen and can be found here.
Continuous integration (CI)
All companies and projects rely on continuous integration (CI) to ensure high quality code and to
avoid regressions. Because this is such a critical piece of every developer's workflow, we wanted to
support it as a first-class feature within moon, and we do just that with the
moon ci command.
How it works
The ci command does all the heavy lifting necessary for effectively running jobs. It achieves this
by automatically running the following steps:
- Determines changed files by comparing the current HEAD against a base.
- Determines all targets that need to run based on changed files.
- Additionally runs affected targets dependencies and dependents.
- Generates an action and dependency graph.
- Installs the toolchain and applicable dependencies.
- Runs all actions within the graph using a thread pool.
- Displays stats about all passing, failed, and invalid actions.
Configuring tasks
By default, all tasks run in CI, as you should always be building, linting, typechecking, testing,
so on and so forth. However, this isn't always true, so this can be disabled on a per-task basis
through the runInCI option.
tasks:
dev:
command: 'webpack server'
options:
runInCI: false
This option must be set to false for tasks that spawn a long-running or never-ending process, like
HTTP or development servers. To help mitigate this, tasks named dev, start, or serve are false
by default.
Integrating
The following examples can be referenced for setting up moon and its CI workflow in popular
providers. For GitHub, we're using our
setup-toolchain action to install moon. For other
providers, we assume moon is an npm dependency and must be installed with Node.js.
- GitHub
- Buildkite
- CircleCI
- TravisCI
name: 'Pipeline'
on:
push:
branches:
- 'master'
pull_request:
jobs:
ci:
name: 'CI'
runs-on: 'ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
with:
fetch-depth: 0
- uses: 'moonrepo/setup-toolchain@v0'
- run: 'moon ci'
steps:
- label: 'CI'
commands:
- 'moon ci'
version: 2.1
jobs:
ci:
docker:
- image: 'cimg/base:stable'
steps:
- 'checkout'
- run: 'moon ci'
workflows:
pipeline:
jobs:
- 'ci'
language: 'node_js'
script: 'moon ci'
Choosing targetsv1.14.0
By default moon ci will run all tasks from all projects that are affected by changed files and
have the runInCI task option enabled. This is a great catch-all
solution, but may not vibe with your workflow or requirements.
If you'd prefer more control, you can pass a list of targets to moon ci, instead of moon
attempting to detect them. When providing targets, moon ci will still only run them if affected by
changed files, but will still filter with the runInCI option.
# Run all builds
$ moon ci :build
# In another job, run tests
$ moon ci :test :lint
Comparing revisions
By default the command will attempt to detect the base and head revisions automatically based on the
current CI provider (powered by the ci_env Rust crate).
If nothing was detected, this will fallback to the configured
vcs.defaultBranch for the base revision, and HEAD for the
head revision.
These values can be customized with the --base and --head command line options, or the
MOON_BASE and MOON_HEAD environment variables, which takes highest precedence.
$ moon ci --base <BRANCH> --head <SHA>
# Or
$ MOON_BASE=<BRANCH> MOON_HEAD=<SHA> moon ci
Parallelizing tasks
If your CI environment supports sharding across multiple jobs, then you can utilize moon's built in
parallelism by passing --job-total and --job options. The --job-total option is an integer of
the total number of jobs available, and --job is the current index (0 based) amongst the total.
When these options are passed, moon will only run affected targets based on the current job slice.
- GitHub
- Buildkite
- CircleCI
- TravisCI
GitHub Actions do not support native parallelism, but it can be emulated using it's matrix.
# ...
jobs:
ci:
# ...
strategy:
matrix:
index: [0, 1]
steps:
# ...
- run: 'moon ci --job ${{ matrix.index }} --job-total 2'
# ...
steps:
- label: 'CI'
parallelism: 10
commands:
# ...
- 'moon ci --job $$BUILDKITE_PARALLEL_JOB --job-total $$BUILDKITE_PARALLEL_JOB_COUNT'
# ...
jobs:
ci:
# ...
parallelism: 10
steps:
# ...
- run: 'moon ci --job $CIRCLE_NODE_INDEX --job-total $CIRCLE_NODE_TOTAL'
TravisCI does not support native parallelism, but it can be emulated using it's matrix.
# ...
env:
global:
- TRAVIS_JOB_TOTAL=2
jobs:
- TRAVIS_JOB_INDEX=0
- TRAVIS_JOB_INDEX=1
script: 'moon ci --job $TRAVIS_JOB_INDEX --job-total $TRAVIS_JOB_TOTAL'
Your CI environment may provide environment variables for these 2 values.
Caching artifacts
When a CI pipeline reaches a certain scale, its run times increase, tasks are unnecessarily ran, and build artifacts are not shared. To combat this, we support remote caching, a mechanism where we store build artifacts in the cloud, and sync these artifacts to machines on demand.
Manual persistence
If you'd prefer to not use remote caching at this time, you can cache artifacts yourself, by
persisting the .moon/cache/{hashes,outputs} directories. All other files and folders in
.moon/cache should not be persisted, as they are not safe/portable across machines.
However, because tasks can generate a different hash each run, you'll need to manually invalidate
your cache. Blindly storing the hashes and outputs directories without a mechanism to invalidate
will simply not work, as the contents will drastically change between CI runs. This is the primary
reason why the remote caching service exists.
Reporting run results
If you're using GitHub Actions as your CI provider, we suggest using our
moonrepo/run-report-action. This
action will report the results of a moon ci run to a pull request as a comment
and workflow summary.
# ...
jobs:
ci:
name: 'CI'
runs-on: 'ubuntu-latest'
steps:
# ...
- run: 'moon ci'
- uses: 'moonrepo/run-report-action@v1'
if: success() || failure()
with:
access-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
The report looks something like the following:
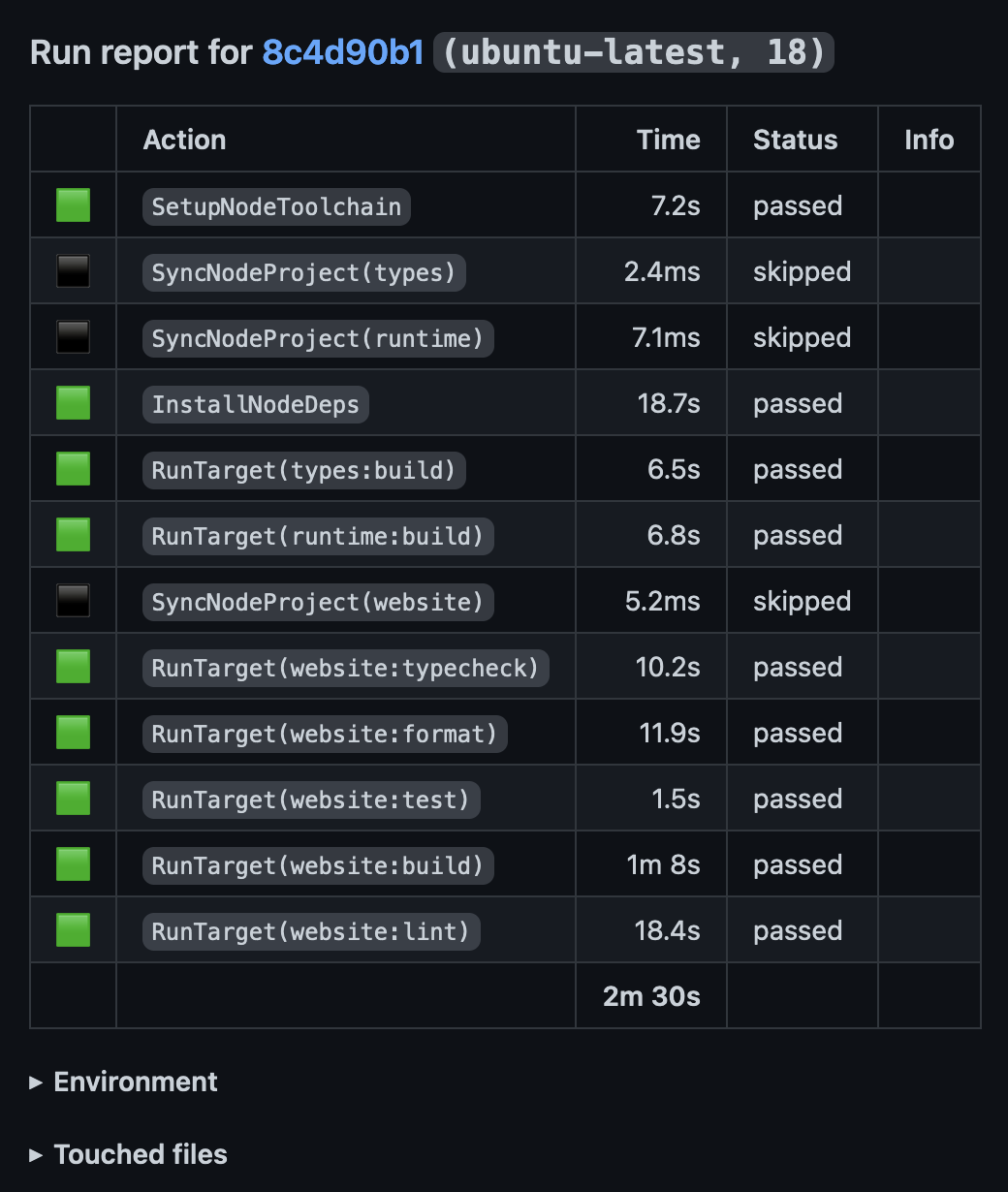
Community offerings
The following GitHub actions are provided by the community:
appthrust/moon-ci-retrospect- Displays the results of amoon cirun in a more readable fashion.kymckay/moon-ci-booster- Displays failingmoon citasks as comments with error logs directly on your pull request.